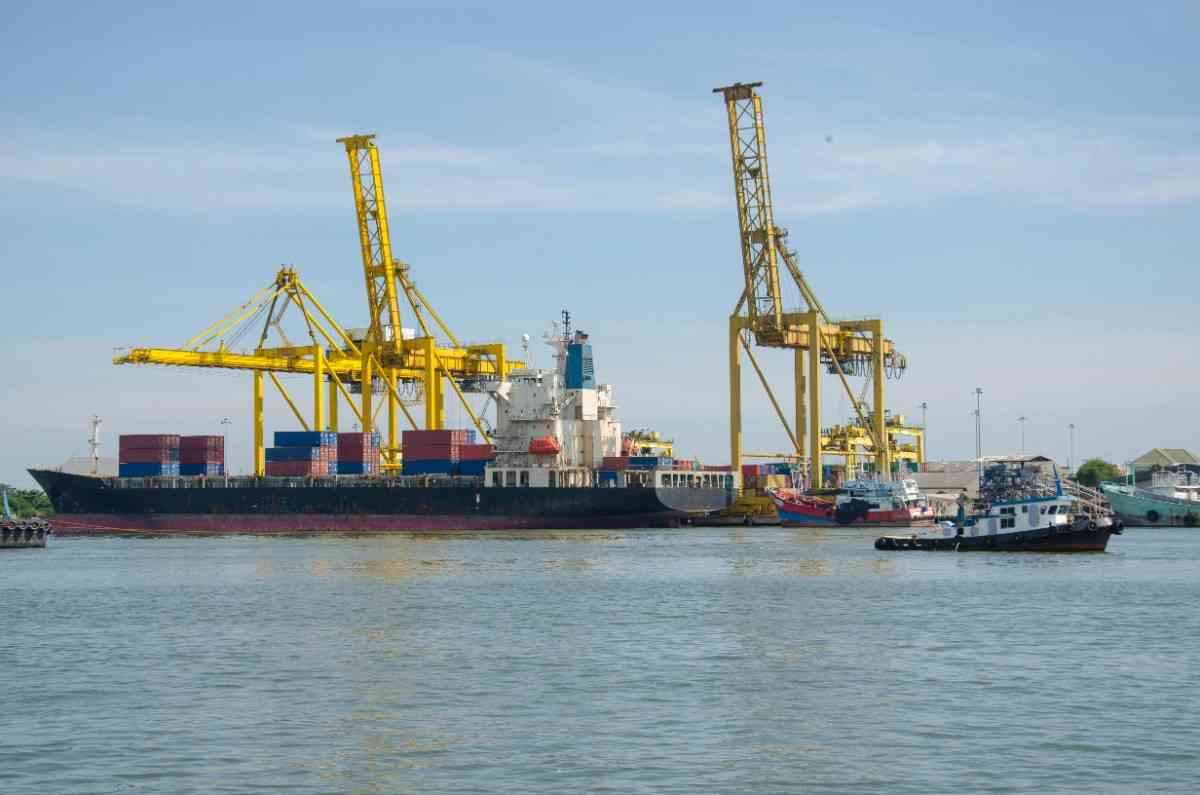
Course Overview
This course offers a thorough understanding of export documentation, covering the essential processes, key players, and critical documents involved in international shipping.
- The Export Guide
- The Role Of The Freight Forwarder/NVOCC
- Terminal Operator Requirements
- Learn About Export Documentation
- Filing & Ocean Cargo Claims
- The Letter Of Credit
What You Will Learn?
Dive into the intricacies of export documentation! This course will equip you with essential skills for managing export processes, understanding key roles, & mastering crucial documents, ensuring you handle shipments efficiently & accurately.
The Export Guide
Gain comprehensive insights into the entire export shipping process, from start to finish, and understand the key roles and responsibilities of the various parties involved in facilitating smooth exports.
The Role Of The Freight Forwarder/NVOCC
Explore the critical services provided by freight forwarders and NVOCCs, and discover how they work alongside shipping lines to coordinate and manage efficient logistics solutions.
Terminal Operator Requirements
Learn how to effectively communicate load details to terminal operators, ensuring that cargo is handled and processed efficiently to meet shipping timelines and operational needs.
Learn About Export Documentation
Master the essential export documents, including the role and functions of the bill of lading, and grasp their significance in ensuring legal compliance and smooth shipment movement.
Filing & Ocean Cargo Claims
Dive into the steps for filing claims related to lost or damaged cargo, understanding the necessary documentation and the importance of timely filing to ensure successful compensation.
The Letter Of Credit
Uncover the intricacies of the letter of credit, including the roles of the parties involved and how this financial instrument secures international trade transactions, reducing risk for both buyers and sellers.
By Artemus Transportation Solutions
With a dedicated legacy since 2004, Artemus Transportation Solutions has become a trusted leader in transportation compliance solutions, offering cutting-edge ISF, AMS, Customs Broker, & eManifest Canada & Japan AFR software. Our years of hands-on industry experience allow us to deliver impactful training courses that go beyond theory, empowering professionals with real-world knowledge.
- 19+ Years of Expertise in Global Transportation Compliance Solutions.
- Practical, real-world insights into Customs, Import, and Export processes.
- Hands-on training in managing complex transportation equipment logistics.
- Efficient solutions for navigating International Shipping and related challenges.

Recognized Certification From Artemus Transportation Solutions
Upon completing the International Shipping course, you'll receive a Certificate of Completion from Artemus Transportation Solutions. This certification highlights your expertise in global shipping processes & compliance, making it a valuable addition to your skills.

Our Reviews
Frequently Asked Questions
Who Is The Course Designed For?
This course is tailored for professionals at all levels, from beginner to intermediate learners, who are looking to enhance their knowledge of global shipping, logistics, & compliance.
What Topics Are Covered In The Export Documentation Course?
The course covers essential export documentation processes, the roles of freight forwarders and NVOCCs, terminal operator requirements, key export documents, filing ocean cargo claims, and understanding the Letter of Credit.
What Are The Essential Export Documents I Need To Know About?
The course covers critical export documents, such as the commercial invoice, packing list, bill of lading, certificate of origin, export licenses, and more, explaining their importance and how they are used in international shipping.
Will I Receive A Certification Upon Course Completion?
Yes, you’ll receive a Certificate of Completion from Artemus Transportation Solutions, which can be showcased on your professional profiles.
Are The Courses Self-Paced Or Instructor-Led?
This course offers a flexible, self-paced learning format with video pre-recorded lessons, allowing you to complete them at your convenience. This approach enables you to learn at your own pace & revisit material as needed.
Do I Need Prior Experience In Shipping Or Logistics To Take This Course?
While prior experience is helpful, our beginner & intermediate-level courses provide foundational knowledge, making them accessible even for those new to the industry.
How Can This Course Benefit My Career?
By completing this course, you’ll gain practical, real-world insights that can boost your skills, enhance your compliance knowledge, & advance your career in the shipping & logistics industry.
What Makes Artemus’s Export Documentation Course Different From Others?
Artemus’s Export Documentation course stands out due to its detailed, practical approach to understanding the intricacies of export documentation. With a focus on real-world scenarios, key players, and actionable insights, the course equips learners with the essential knowledge needed to handle export processes efficiently and compliantly.
Export Documentation Course: Explore export-focused topics and documentation basics
What does a freight forwarder do? understanding their role in global trade
A freight forwarder acts as an intermediary between shippers and transportation services, ensuring goods move efficiently across borders. They handle documentation, customs clearance, and logistics coordination, making international trade smoother. Their expertise helps businesses navigate complex regulations, reduce costs, and avoid shipping delays. Freight forwarders also offer additional services like cargo insurance, warehousing, and packaging solutions. Their role is crucial in optimizing supply chain operations for exporters and importers alike.
What do freight forwarders do? key responsibilities explained
Freight forwarders manage the logistics of transporting goods from one country to another. Their responsibilities include booking cargo space, arranging transport modes, handling documentation, and ensuring compliance with international shipping laws. They negotiate freight rates, track shipments, and provide solutions for any transport-related issues. By leveraging their network and expertise, they help businesses streamline global trade operations and improve supply chain efficiency.
What freight forwarders do? an overview of their services
Freight forwarders provide end-to-end shipping solutions, including route planning, cargo handling, and customs brokerage. They assist in securing competitive freight rates and selecting the most cost-effective shipping methods. Their expertise extends to regulatory compliance, risk management, and tracking shipments to ensure timely delivery. They play a crucial role in international trade by simplifying logistics and helping businesses navigate global supply chain challenges.
How does freight forwarding work? step-by-step process
Freight forwarding involves multiple steps, starting with booking cargo space with carriers. The forwarder then prepares necessary shipping documents, arranges transportation, and ensures customs clearance. Once the goods are shipped, they provide tracking updates and handle any potential delays or issues. Upon arrival, they coordinate delivery to the final destination. Their expertise ensures smooth operations, reducing risks and costs for businesses.
NVOCC freight forwarder: what makes them different?
A Non-Vessel Operating Common Carrier (NVOCC) acts as both a freight forwarder and a carrier, issuing their own bill of lading. Unlike traditional freight forwarders, NVOCCs buy large volumes of space from ocean carriers and resell it to shippers. They offer more control over shipping schedules, but they also take on higher financial responsibility. Understanding the difference between NVOCCs and freight forwarders can help businesses choose the best logistics partner for their needs.
Difference between NVOCC and freight forwarder: key distinctions
An NVOCC operates as a carrier without owning ships, issuing its own bill of lading, while a freight forwarder acts as an agent, arranging transport with multiple carriers. NVOCCs take on higher financial responsibility, whereas freight forwarders focus on managing logistics and customs clearance. Choosing between the two depends on shipping volume, cost considerations, and service requirements.
Terminal operator: their role in export and import logistics
A terminal operator manages cargo handling at ports, ensuring smooth loading and unloading of containers. They coordinate with shipping lines, customs authorities, and logistics providers to maintain port efficiency. Terminal operators use advanced technology to track shipments, reduce congestion, and optimize cargo flow. Their role is essential in maintaining global supply chain efficiency and preventing shipment delays.
Documentation required for import and export business: essential paperwork
Import and export businesses require various documents, including a commercial invoice, bill of lading, packing list, and certificate of origin. Customs authorities also require import/export declarations and any relevant permits or licenses. Proper documentation ensures compliance with international trade regulations and prevents shipping delays. Working with a freight forwarder or customs broker can simplify the process and reduce errors.
Export documentation: key documents for smooth international trade
Export documentation includes critical paperwork such as the bill of lading, commercial invoice, packing list, and export declaration. These documents ensure compliance with customs regulations and facilitate smooth cross-border transactions. Proper documentation helps avoid shipping delays, penalties, or rejected shipments. Businesses should stay updated on regulatory changes to ensure smooth export operations.
Documents needed for export: a checklist for shippers
Exporters must prepare essential documents such as the commercial invoice, packing list, bill of lading, certificate of origin, and export license. Additional documents may be required depending on the destination country, such as health or safety certificates for specific goods. Ensuring all paperwork is complete and accurate helps prevent delays and legal issues.
Documents needed to export: understanding regulatory requirements
Exporting goods requires compliance with international trade laws. Key documents include an export declaration, transport documents, and any required trade agreements or permits. These documents help verify the authenticity of shipments and ensure smooth customs clearance. Proper documentation also plays a vital role in securing payments from international buyers.
Documents required for export: ensuring compliance and efficiency
Exporting requires several essential documents, including customs declarations, shipping instructions, and invoices. Failure to provide the correct paperwork can result in shipment holds or fines. Understanding export requirements for different countries helps businesses avoid complications. Many companies use digital export management systems to streamline documentation.
Documents required to export: mandatory paperwork for global trade
International trade regulations mandate exporters to provide specific documentation, such as commercial invoices, bills of lading, and export licenses. Some countries require additional documents, like quality inspection certificates or product-specific approvals. Keeping track of these requirements ensures smooth transactions and minimizes disruptions in global trade.
Export document requirements: what businesses need to know
Export documents verify the legality, quantity, and value of shipments. Essential documents include proforma invoices, shipping bills, and certificates of compliance. Failure to provide accurate documentation can lead to customs delays or additional fees. Staying informed about export regulations can help businesses maintain efficiency in international trade.
Export documents: key paperwork for successful global trade
Export documents facilitate the legal movement of goods across international borders. They include transportation, financial, and regulatory documents that ensure customs compliance. Businesses must ensure accuracy in documentation to prevent shipment rejections or delays. Digital documentation systems can help simplify the process and enhance efficiency.
Customs export documentation: ensuring smooth border clearance
Customs export documentation includes critical paperwork such as export declarations, shipping invoices, and regulatory certificates. Accurate documentation is necessary for customs authorities to verify shipments and apply appropriate duties or tariffs. Businesses should work with experienced freight forwarders or customs brokers to ensure compliance and avoid penalties.
Letter of credit: securing payments in international trade
A letter of credit (LC) is a financial guarantee issued by a bank, ensuring that a seller receives payment once specific terms are met. It minimizes the risk for both buyers and sellers in global transactions. LCs are commonly used in high-value exports where trust between trading partners is limited.
What is a letter of credit? definition & benefits
A letter of credit is a payment mechanism that guarantees sellers receive funds once they fulfill contractual obligations. Banks act as intermediaries, reducing the risk of non-payment in international trade. It provides security to both parties by ensuring compliance with agreed-upon terms before releasing funds.
What is the meaning of letter of credit? key terms explained
A letter of credit is a legally binding agreement issued by a bank that ensures exporters receive payment for shipped goods. The bank verifies that all conditions specified in the agreement are met before releasing funds. It is widely used in global trade to mitigate risks and build trust.
How does a letter of credit work? step-by-step process
A letter of credit involves multiple parties, including the buyer, seller, issuing bank, and advising bank. The buyer’s bank issues the LC to guarantee payment. Once the seller meets all contractual conditions and submits the required documents, the bank releases the funds. This process ensures secure and smooth international transactions.
AES export filing: why it’s essential for exporters
Automated Export System (AES) filing is required for certain exports from the U.S. It ensures accurate tracking of shipments and compliance with trade regulations. Exporters must submit Electronic Export Information (EEI) through AES for goods exceeding specific value thresholds. Proper AES filing helps prevent penalties and facilitates smoother customs clearance.
Automated export system filing: streamlining trade compliance
The Automated Export System (AES) is an electronic platform used to report export data to the U.S. government. It is essential for compliance with export control laws and tracking international shipments. Exporters must file accurate information to avoid fines and delays in the shipping process.
FAQs
-
What is export documentation, and why is it important?
Export documentation consists of essential paperwork required for international trade. It ensures compliance with customs regulations, facilitates smooth shipping, and helps exporters receive payments. Proper documentation reduces the risk of delays, fines, or shipment rejections.
-
What are the key documents required for exporting goods?
The main documents required for export include:
- Commercial Invoice – Lists details of the goods sold.
- Packing List – Specifies packaging details and contents.
- Bill of Lading – A contract between the exporter and the carrier.
- Export Declaration – Required for customs clearance.
- Certificate of Origin – Verifies the country of manufacture.
Additional documents may be needed based on the product type and destination country.
-
What is a Bill of Lading, and why is it necessary?
A Bill of Lading (BOL) is a legal document issued by the carrier that serves as a shipment receipt and transport contract. It includes details about the exporter, importer, and goods being shipped. The BOL is necessary for customs clearance and ensures the cargo is delivered to the right recipient.
-
What is the difference between a proforma invoice and a commercial invoice?
A proforma invoice is a preliminary document that provides an estimate of costs before the goods are shipped. A commercial invoice is the final document issued after shipment, containing the actual sale details, required for customs clearance and payment processing.
-
What is a Letter of Credit, and how does it work?
A Letter of Credit (LC) is a financial guarantee issued by a bank ensuring payment to the exporter once the shipment meets the agreed conditions. The bank verifies all required documents before releasing funds, reducing the risk of non-payment.
-
What is AES filing, and when is it required?
AES (Automated Export System) filing is a mandatory electronic submission for U.S. exports exceeding a specific value threshold. It ensures compliance with trade regulations and helps track outbound shipments. Exporters must file Electronic Export Information (EEI) through AES for eligible shipments.
-
How can I ensure my export documents are accurate?
To avoid errors, double-check all information, including product descriptions, HS codes, consignee details, and value declarations. Work with a freight forwarder or customs broker to ensure compliance with regulations and prevent shipment delays.
-
What happens if my export documentation is incorrect or incomplete?
Incorrect or missing documentation can result in customs delays, fines, or rejection of goods. It may also lead to additional charges for storage and resubmission. Ensuring accuracy in documentation helps avoid legal and financial risks.